Access data with managed identity - Azure App Service
November 05, 2021 by Anuraj
AspNetCore Azure SqlServer
This post is about connecting and accessing data from SQL Service using Azure App Service Managed Identity feature. Azure SQL supports Azure AD authentication, which means it also supports the Managed Identity feature of Azure AD. With Managed Identity, we no longer need the User Id and Password as part of your connection string. The credential is managed automatically by Azure and allows us to connect to resources.
First you need to create the SQL Server and SQL Database with SQL Server authentication. Once it is done, you can create Azure App Service. And then you need to enable identity in the app service. You can do this from Identity menu of the App Service. Right now I am using System Assigned - A system assigned managed identity is restricted to one per resource and is tied to the lifecycle of this resource. You can grant permissions to the managed identity by using Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC). The managed identity is authenticated with Azure AD, so you don’t have to store any credentials in code. Once you enable the Identity, you will get an Object Id.
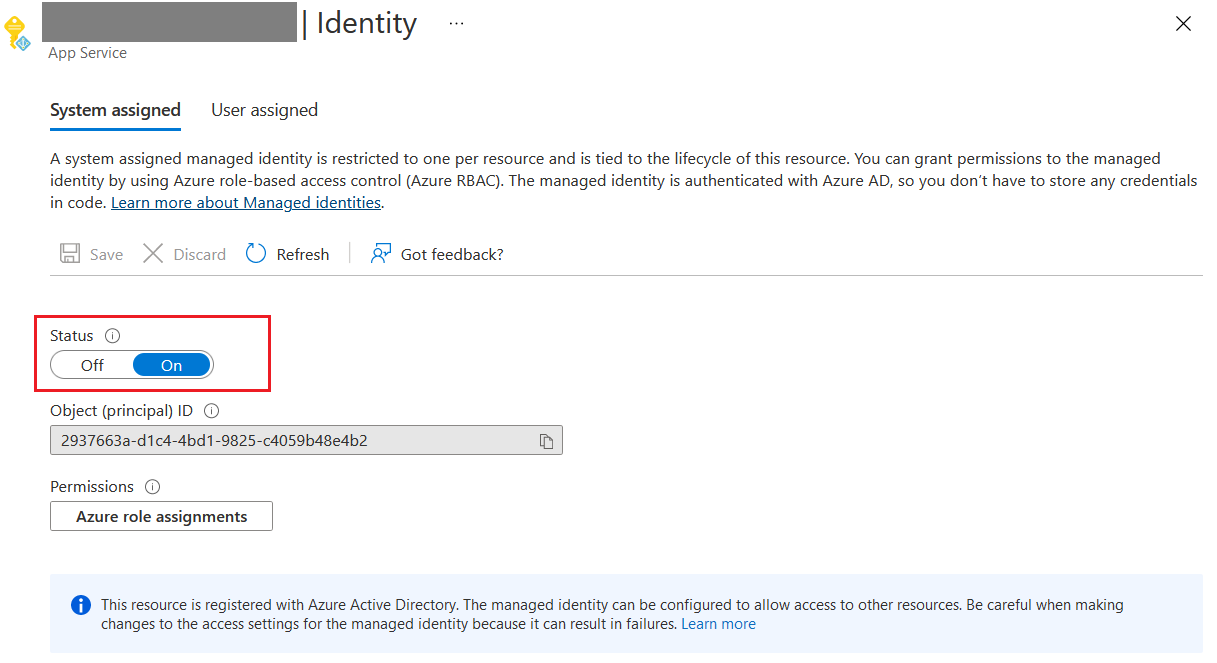
Next you can configure the Identity to your SQL Server. To do this, select the SQL Server and select the Azure Active Directory option.
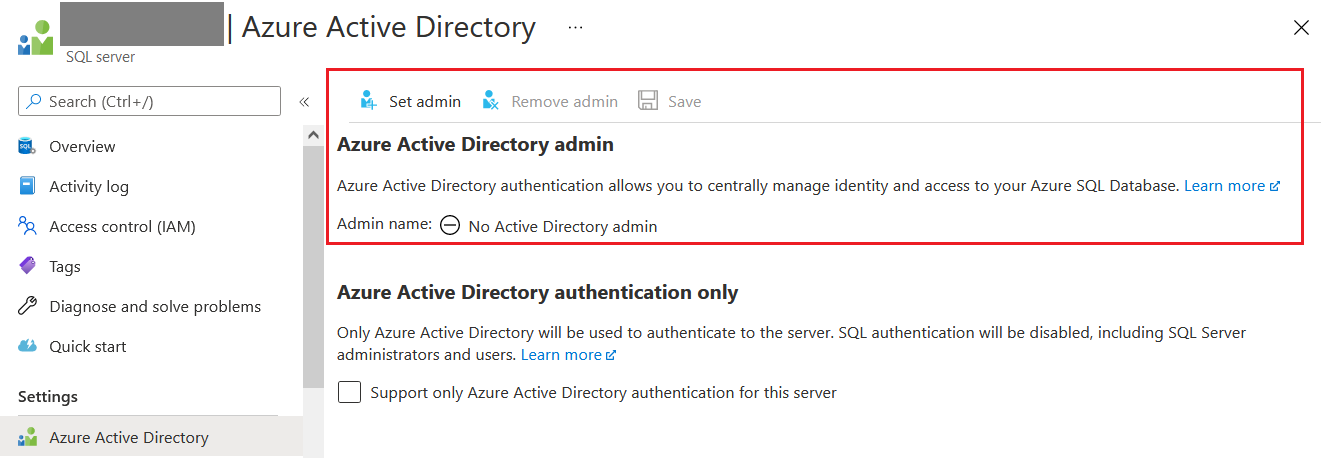
By default there won’t be any users, you can click on the set admin option and from the Azure Active Directory user list, search for the Object Id - which from the App Service. And then click Select button and select the user as Azure Active Directory admin for the Sql Server.
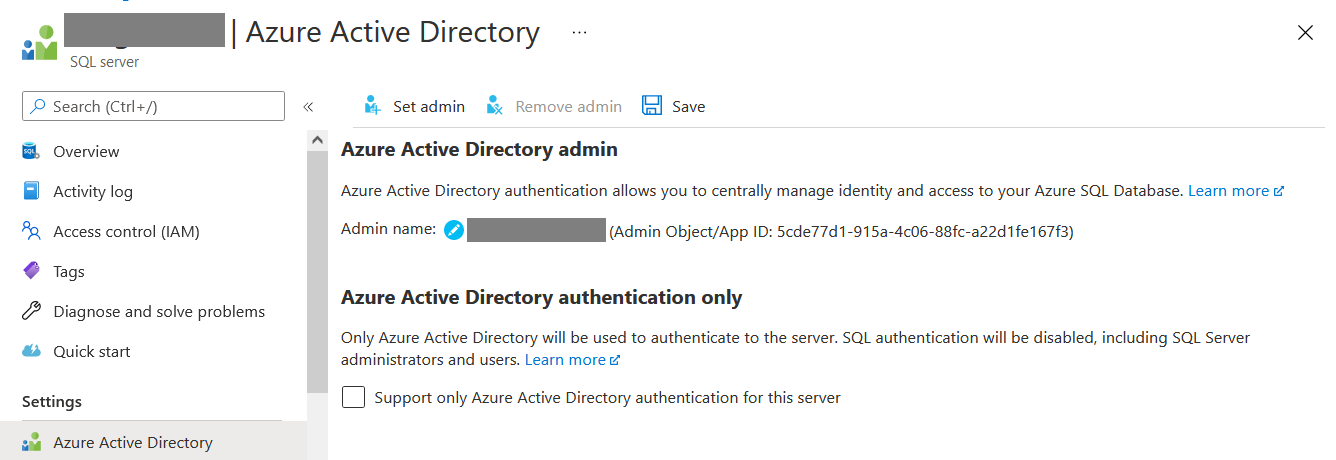
Next you need to configure some permissions for the web app to the database. You can connect with Sql Server Management Studio or the query editor in Azure Portal and execute following code.
ALTER ROLE db_datareader ADD MEMBER [app-service-name];
ALTER ROLE db_datawriter ADD MEMBER [app-service-name];
ALTER ROLE db_ddladmin ADD MEMBER [app-service-name];And finally you can modify the code in your database context like this.
public class MyDatabaseContext : DbContext
{
public MyDatabaseContext(DbContextOptions<MyDatabaseContext> options)
: base(options)
{
var connection = (Microsoft.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection)Database.GetDbConnection();
var credential = new DefaultAzureCredential();
var token = credential
.GetToken(new Azure.Core.TokenRequestContext(
new[] { "https://database.windows.net/.default" }));
connection.AccessToken = token.Token;
}
public DbSet<Todo> Todo { get; set; }
}Now you’re done with the configuration. You can modify the connection string like this - remove the User Id and Password.
Using Managed Identities you can connect to SQL Server without configuring the user name and password which helps you to improve your application security and management of credential management can be avoided.
Happy Programming :)
Found this useful? Share it with your network!
Copyright © 2026 Anuraj. Blog content licensed under the Creative Commons CC BY 2.5 | Unless otherwise stated or granted, code samples licensed under the MIT license. This is a personal blog. The opinions expressed here represent my own and not those of my employer. Powered by Jekyll. Hosted with ❤ by GitHub
