Anti-forgery validation with asp dotnet core and angular
August 04, 2018 by Anuraj
ASP.NET Core Angular
This post is about enabling Anti-forgery validation in single page applications using ASP.NET Core and Angular. The anti-forgery token can be used to help protect your application against cross-site request forgery. In earlier versions of ASP.NET, you had to explicitly decorate a controller or an action method to enable Anti-forgery, in ASP.NET Core Web API all the unsafe methods(PUT, POST) anti-forgery validation is enabled by default.
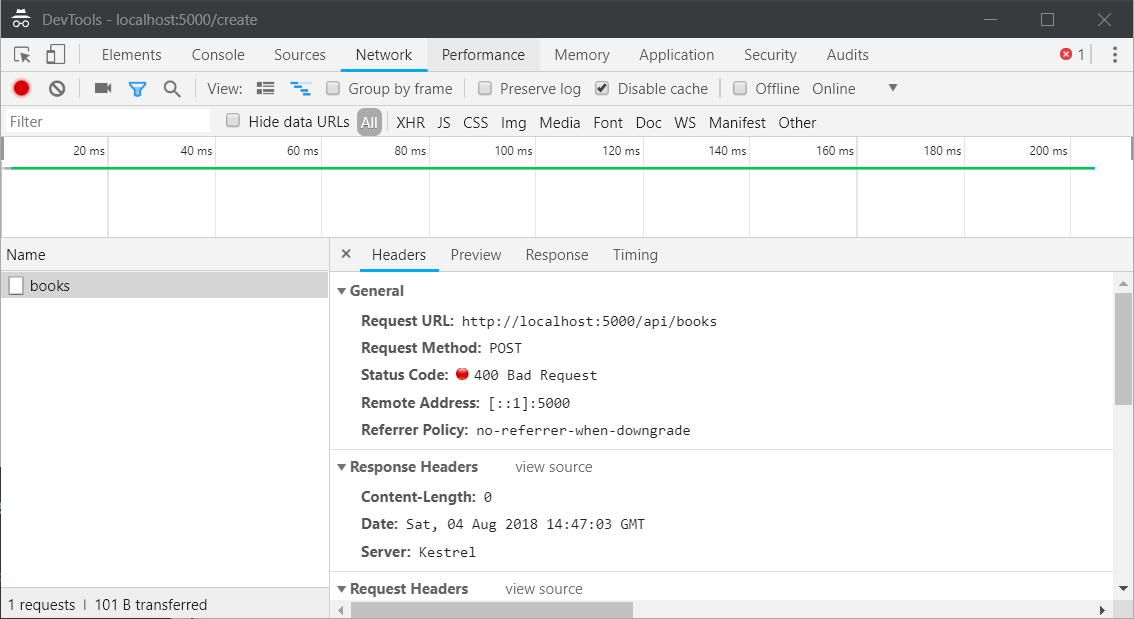
AngularJS uses a convention to address CSRF. If the server sends a cookie with the name XSRF-TOKEN, the AngularJS $http service adds the cookie value to a header when it sends a request to the server. This process is automatic. The header doesn’t need to be set explicitly. The header name is X-XSRF-TOKEN. The server should detect this header and validate its contents.
So first you need to enable server to detect XSRF-TOKEN from Angular application as the anti-forgery token value, you can do this by modifying Startup class, ConfigureServices method.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddAntiforgery(options => options.HeaderName = "X-XSRF-TOKEN");
services.AddDbContext<BooksApiDbContext>(options => options.UseInMemoryDatabase("BooksDb"));
services.AddMvc()
.AddJsonOptions(options => options.SerializerSettings.ContractResolver = new DefaultContractResolver());
}Now your ASP.NET Core app knows about the token which is sent along with Request as header. Next you need to set a cookie, with the token value, so that it can process the request. You can do this using adding a middleware delegate like this.
app.Use(next => context =>
{
if (context.Request.Path.Value.IndexOf("/api", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) != -1)
{
var tokens = antiforgery.GetAndStoreTokens(context);
context.Response.Cookies.Append("XSRF-TOKEN", tokens.RequestToken,
new CookieOptions() { HttpOnly = false });
}
return next(context);
});So when a request hit ASP.NET Core Web API, server will read the Angular XSRF-TOKEN token and create and set the cookie.
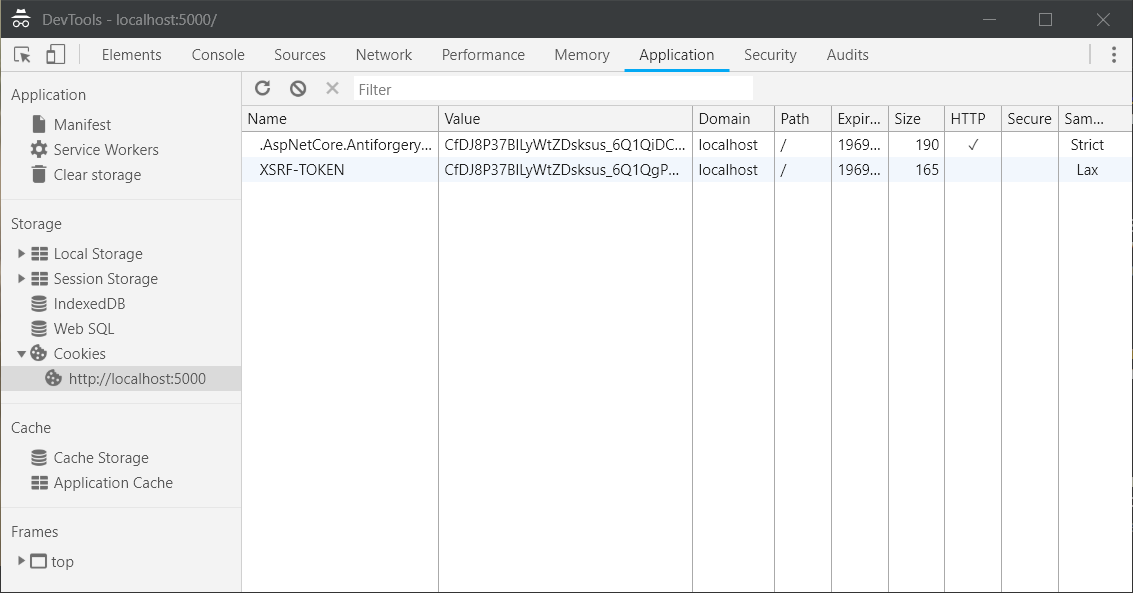
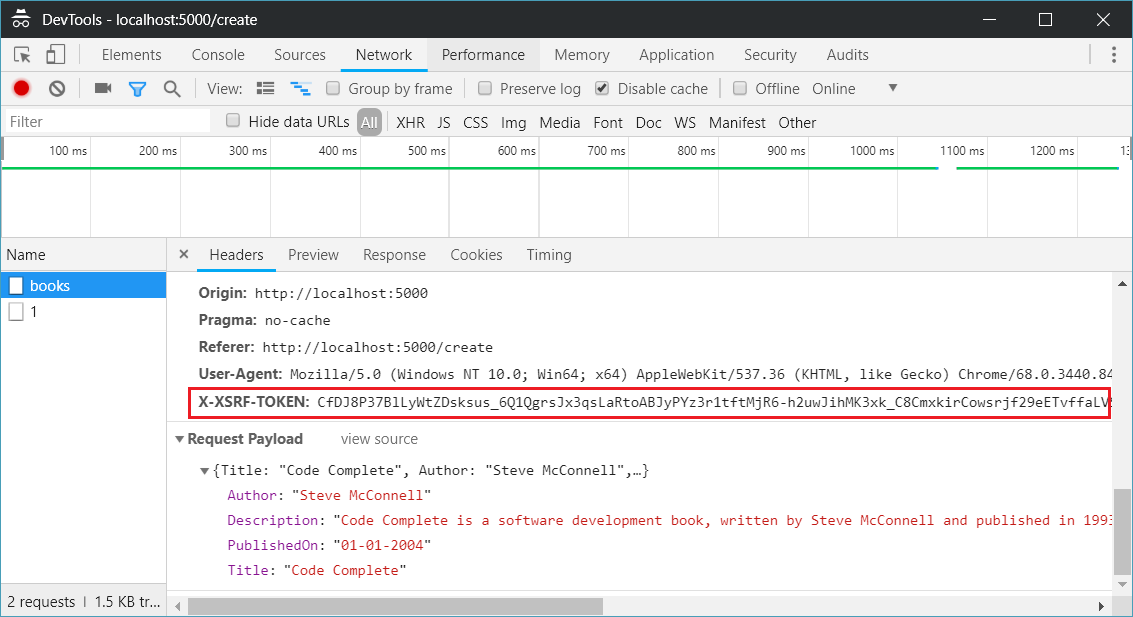
Next any request from Angular, you will be able to see the X-XSRF-TOKEN.
Happy Programming :)
Found this useful? Share it with your network!
Copyright © 2026 Anuraj. Blog content licensed under the Creative Commons CC BY 2.5 | Unless otherwise stated or granted, code samples licensed under the MIT license. This is a personal blog. The opinions expressed here represent my own and not those of my employer. Powered by Jekyll. Hosted with ❤ by GitHub
