How to Build an Email Sentiment Analysis Bot - Using Azure Functions
March 14, 2021 by Anuraj
Azure Serverless Cognitive Services
This is part two of the post on building an Email Sentiment Analysis Bot with the help of Azure Serverless tools and Azure Cognitive Services. In the earlier post Logic Apps were using. In this post you will learn how to use Azure Functions instead of Logic Apps.
How it works
In this implementation, you will be using Azure Function Http Trigger. And in the Azure Function, you can use Azure Cognitive service for analyzing the sentiment. And Azure Function output binding to store the data to Azure Table storage. You can scale this solution using Durable Functions instead of a single function.
Implementation
Unlike Logic App, Azure Functions doesn’t have a trigger for incoming emails. You need some applications on which you’re able to receive emails as well as send notifications. SendGrid is one of such application which offers a free account as well. So you need to create a SendGrid account first.
Creating a SendGrid account
You can do create a SendGrid account from Azure portal. Click on New Resource and search for SendGrid and select SendGrid.
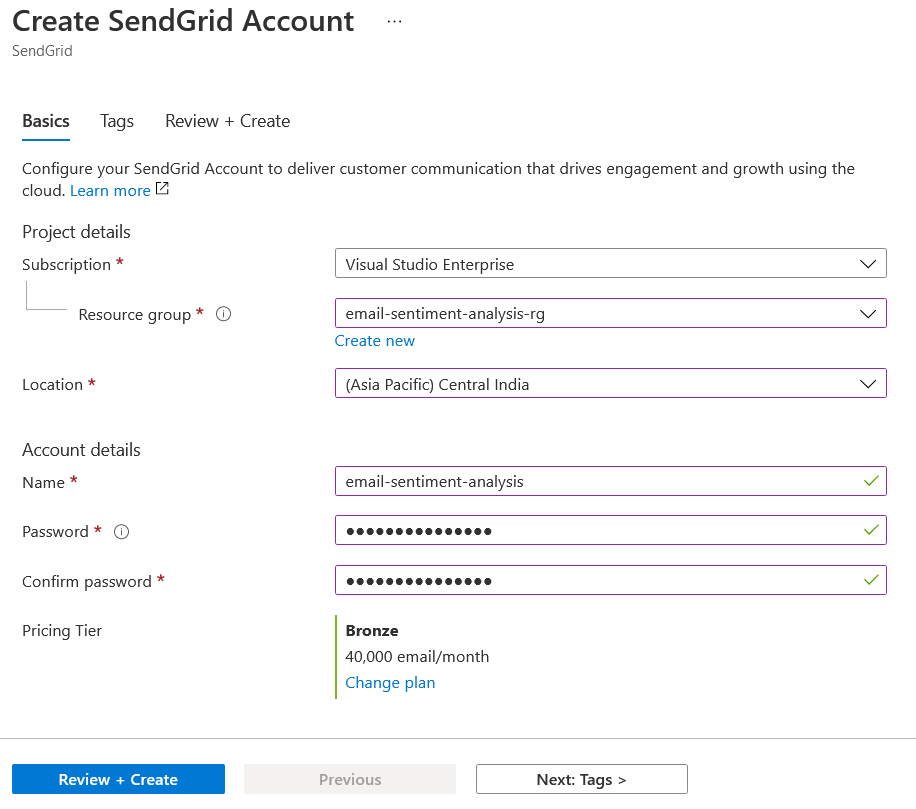
You need to configure name, password and your other details like first name, last name etc and select the Plan as Free. The click on the Create button. Once you created the account, you can login to SendGrid app with the credentials. Next you need to create an Azure Function, you can use any language to do this, C# and .NET used in this post.
Creating a Azure Function
To create an Azure function, you can search for Function App in Azure, then select and create a new function app.
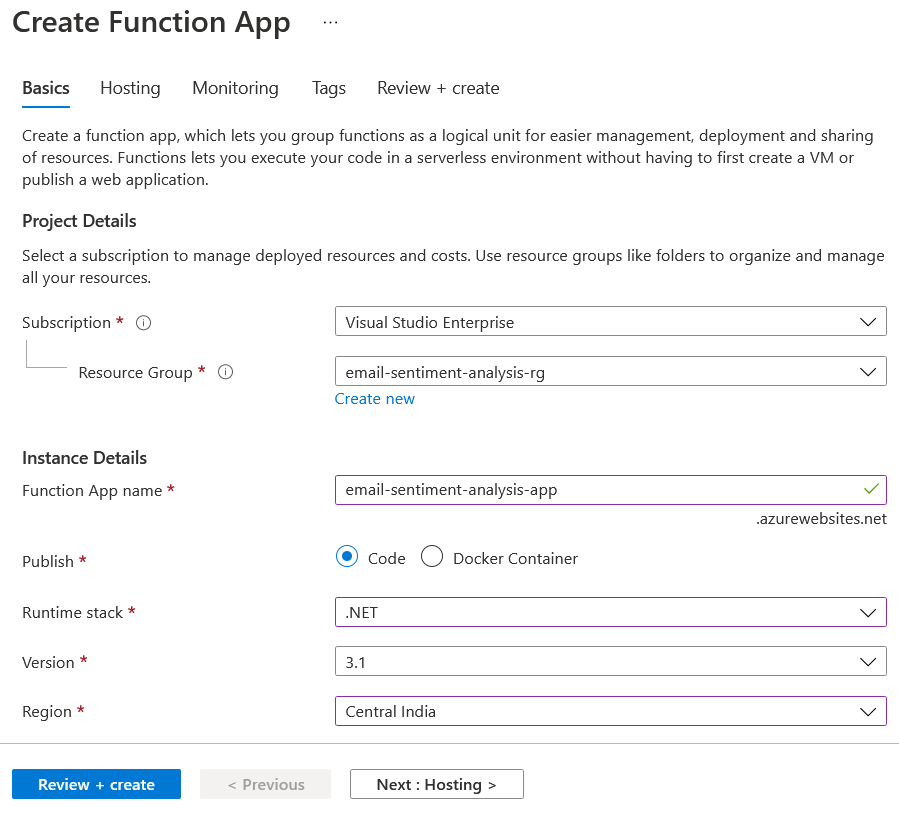
You can choose Consumption Plan, and .NET as the Runtime Stack. Once you create a function app, you need to create an HTTP Trigger function.
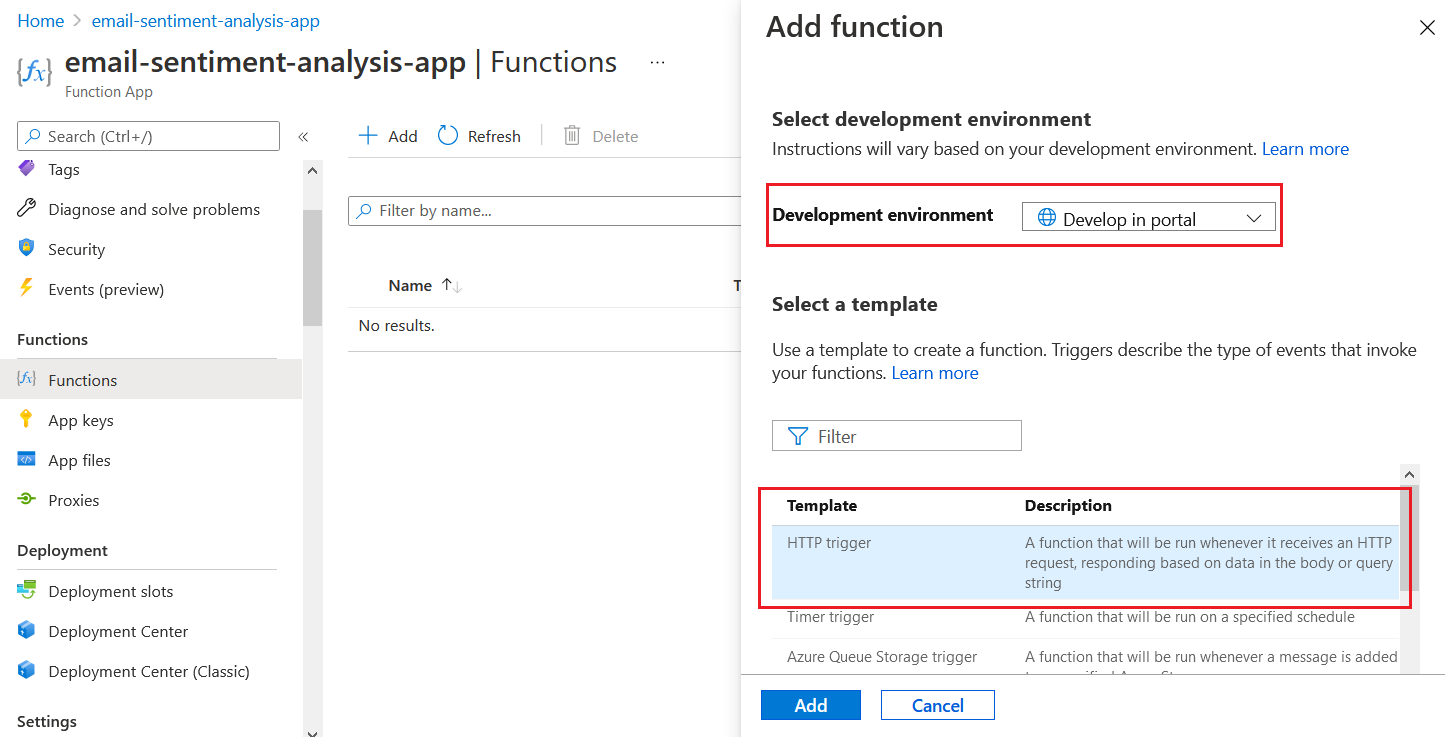
You can select the option, Develop in Portal and HttpTrigger as template. You can provide the name and authorization level, you can choose Function. Next you can click on the Add button. Once you create the Http Template function, click on the function name from the list. Then select the Code + Test option under Developer menu.
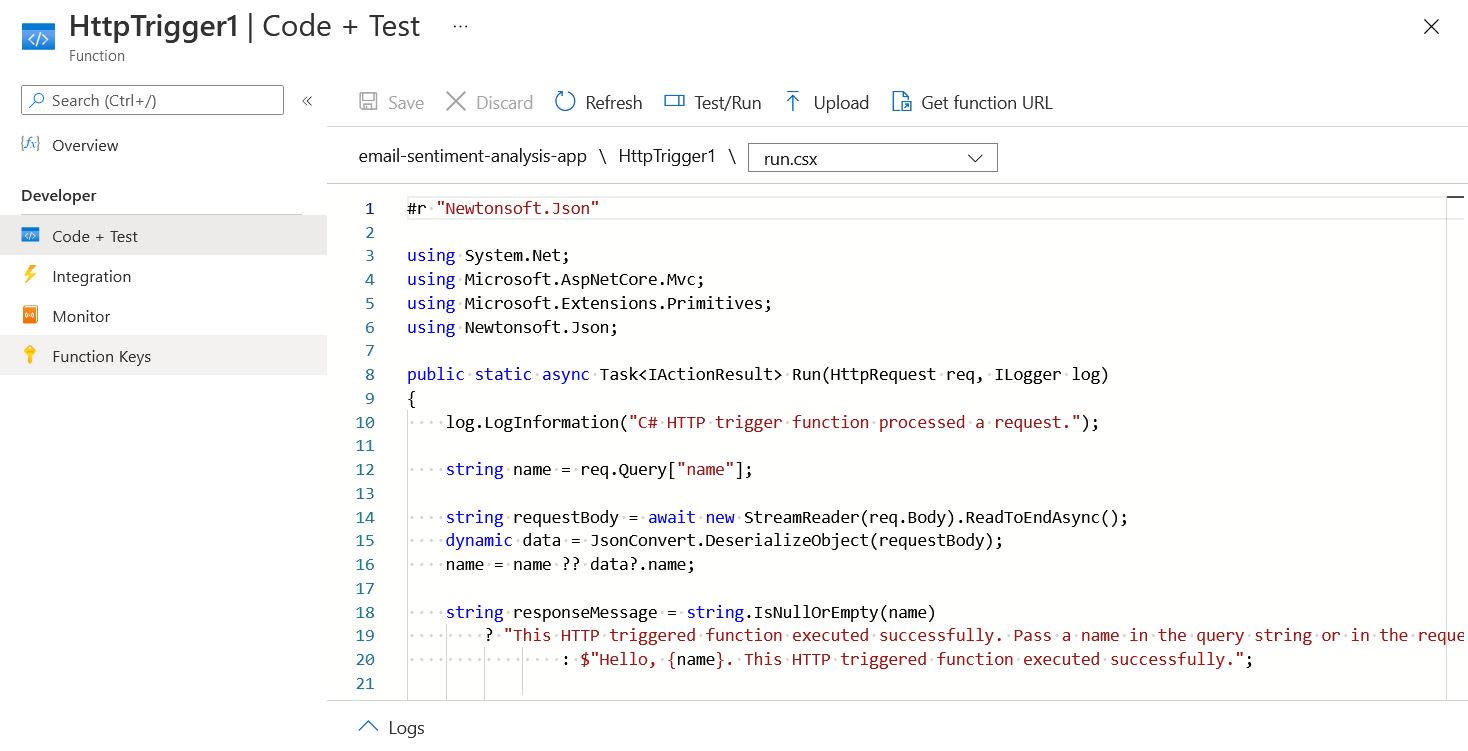
You can click on the Get Function URL menu and you can test it from your browser. The function app executed for both HTTP POST and GET methods. It is expecting a name object. You can send it in with your post method body or as query string. So you completed the Azure function implementation. Next you need to configure SendGrid account to send notification - HTTP POST - when you receive an email to this Azure Function you created.
Configuring SendGrid and Azure Function
To integrate SendGrid and Azure Function you need to use SendGrid Inbound parse configuration. There is a blog post - Building mailinator clone using SendGrid and ASP.NET Core already available on this topic, visit it for the initial setup and configuration. Once the configuration is completed, choose the Inbound Parse option from SendGrid Account settings.
Click on the Add Host & URL option and provide the Azure Function URL in the Destination URL. Once you added it, you will be able to see it in the list. Next you need to modify the Azure Function to receive the HTTP POST from SendGrid when an email received. You can use the same code in the earlier blog post as it is in the Azure function.
Converting form data to JSON
In the blog the IFormCollection is converted to a POCO class using Reflection, so that you can run parse the incoming post data and run sentiment analysis on the body.So you need a model class like this which is based on SendGrid Payload information.
public class EmailModel
{
public string Headers { get; set; }
public string Dkim { get; set; }
public string To { get; set; }
public string Html { get; set; }
public string From { get; set; }
public string Text { get; set; }
public string Sender_Ip { get; set; }
public string SPF { get; set; }
public string Attachments { get; set; }
public string Subject { get; set; }
public string Envelope { get; set; }
public string Charsets { get; set; }
}Here is the function which converts the IFormCollection to C# object.
public static T Map<T>(IFormCollection formCollection) where T : new()
{
var t = new T();
var properties = t.GetType().GetProperties();
foreach (var property in properties)
{
var propertyValue = formCollection.TryGetValue(property.Name, out var output) ? output[0] :
property.PropertyType.IsValueType ? Activator.CreateInstance(property.PropertyType) : null;
property.SetValue(t, propertyValue, null);
}
return t;
}And finally you can modify the function code like this.
public static async Task<IActionResult> Run(HttpRequest req, ILogger log)
{
log.LogInformation("C# HTTP trigger function processed a request.");
var collection = await req.ReadFormAsync();
var email = Map<EmailModel>(collection);
//Send the email.Text property for processing in Text Analytics.
return new OkObjectResult("Function Executed");
}Next you need to write the code to analyse sentiment of the email.Text property.
Running Text Analytics on the email
To run sentiment analysis on the email body first you need to reference the Azure.AI.TextAnalytics package to your function app. To add a nuget package to a CSX function, you need to create a function.csproj using Kudu with the following content.
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk">
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>netstandard2.0</TargetFramework>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Azure.AI.TextAnalytics" Version="5.1.0-beta.5" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>This proj file will reference the nuget package to your function. And you can modify the function like this.
private static readonly AzureKeyCredential credentials = new AzureKeyCredential("<replace-with-your-text-analytics-key-here>");
private static readonly Uri endpoint = new Uri("<replace-with-your-text-analytics-endpoint-here>");
public static async Task<IActionResult> Run(HttpRequest req, ILogger log)
{
log.LogInformation("C# HTTP trigger function processed a request.");
var client = new TextAnalyticsClient(endpoint, credentials);
var collection = await req.ReadFormAsync();
var email = Map<EmailModel>(collection);
var documentSentiment = client.AnalyzeSentiment(email.Text);
//Send the email.Text property for processing in Text Analytics.
log.LogInformation($"Document sentiment: {documentSentiment.Value.Sentiment}");
return new OkObjectResult($"Document sentiment: {documentSentiment.Value.Sentiment}");
}The AnalyzeSentiment method will run sentiment analysis on the text and return the string value whether it is positive or negative or neutral. So you don’t need to create custom column for Power BI display.
There are some limitations to the number of characters for example - Text Analytics only supports the maximum size of a single document is 5,120 characters. So it is recommended to do a check and modify the logic to avoid exceptions. You can do something like this.
var size = 5000;
var docs = Enumerable.Range(0, text.Length / size).Select(i => text.Substring(i * size, size));
client.AnalyzeSentimentBatch(docs);Now you have completed the sentiment analysis feature as well. Next you need to write code to save the information to Azure Table Storage.
Writing the sentiment analysis results to Azure Table Storage
You can click on the Integration menu. You will be able to see the Triggers, Input Binding and Output bindings in the screen. You can click on the Add Output option. And you need to select Azure Table Storage for Binding Type and modify the table name with the Azure Table storage - Table name.
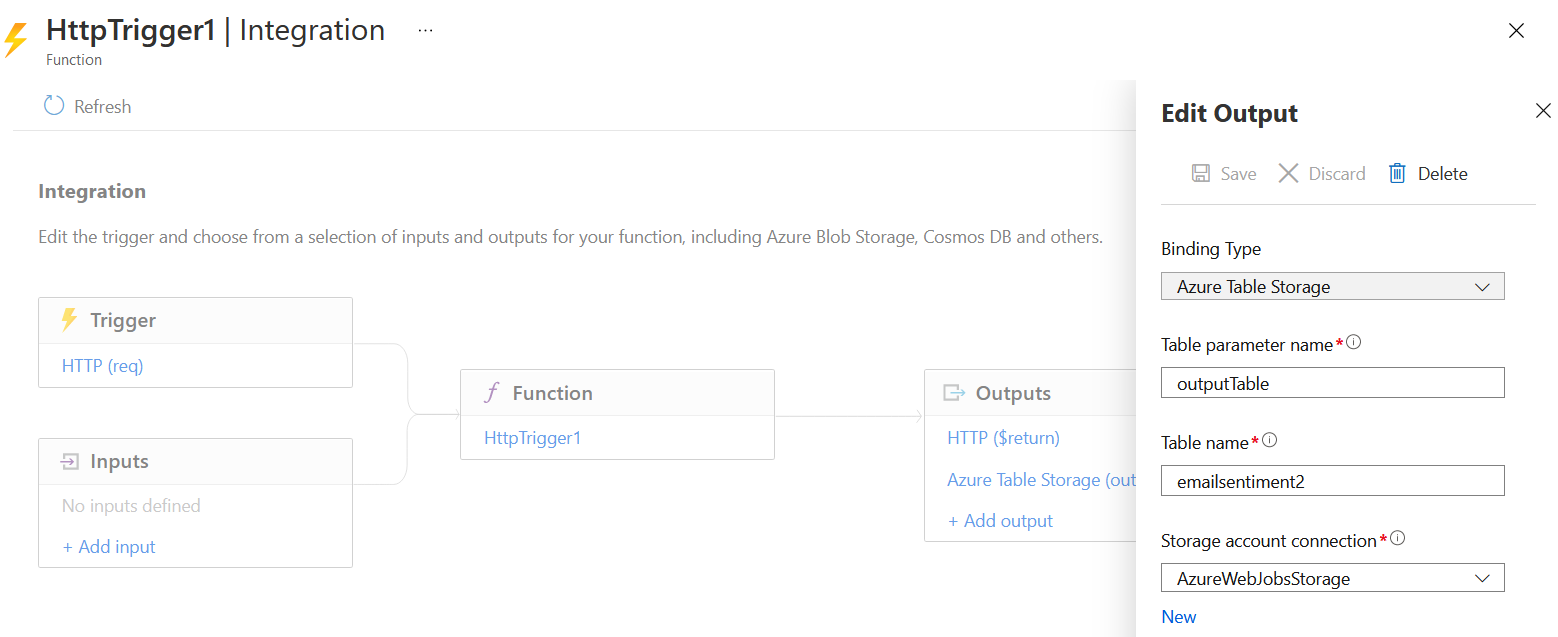
You can modify the Azure Function - run() method parameter and you can store the data to Table storage.
public static async Task<IActionResult> Run(HttpRequest req, ICollector<EmailSentiment> outputTable, ILogger log)
{
log.LogInformation("C# HTTP trigger function processed a request.");
var client = new TextAnalyticsClient(endpoint, credentials);
var collection = await req.ReadFormAsync();
var email = Map<EmailModel>(collection);
var documentSentiment = client.AnalyzeSentiment(email.Text);
var id = Guid.NewGuid().ToString("N");
outputTable.Add(new EmailSentiment()
{
PartitionKey = id,
RowKey = id,
Id = id,
Sentiment = documentSentiment.Value.Sentiment.ToString() }
);
return new OkObjectResult($"Document sentiment: {documentSentiment.Value.Sentiment}");
}The table storage will be injected to the function as parameter and you will be able to insert data to that. And here is the EmailSentiment class.
public class EmailSentiment
{
public string PartitionKey { get; set; }
public string RowKey { get; set; }
public string Id { get; set; }
public string Sentiment { get; set; }
}Now you can use the storage account and display the data in Power BI.
In this blog post you explored about running sentiment analysis on email using Azure Functions. Both Logic Apps and Azure Functions has its own pros and cons. And can be used based on your requirement. If you want to more control on the implementation you need to use Azure Functions.
Happy Programming :)
Found this useful? Share it with your network!
Copyright © 2026 Anuraj. Blog content licensed under the Creative Commons CC BY 2.5 | Unless otherwise stated or granted, code samples licensed under the MIT license. This is a personal blog. The opinions expressed here represent my own and not those of my employer. Powered by Jekyll. Hosted with ❤ by GitHub
