Getting started with Cosmos DB SQL Provider for Entity Framework Core
August 31, 2018 by Anuraj
ASPNET Core Cosmos DB EF Core
This post is about working with Cosmos DB SQL Provider for Entity Framework Core. Azure Cosmos DB is Microsoft’s globally distributed, multi-model database. With the click of a button, Azure Cosmos DB enables you to elastically and independently scale throughput and storage across any number of Azure’s geographic regions.
First you need to install the EF Core provider for Cosmos DB. You can get it from NuGet.
Once you install it via dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Cosmos.Sql --version 2.2.0-preview1-35029. Once you install it, you can modify the Startup class code.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddEntityFrameworkCosmosSql();
services.AddDbContextPool<BookmarksDbContext>(options =>
options.UseCosmosSql(new Uri(Configuration["CosmosDb:EndpointURI"]),
Configuration["CosmosDb:PrivateKey"], "BookmarksDb"));
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_1);
}For this post I am using Cosmos DB emulator. I am reading it from appsettings.json file. Here is the Endpoint URI and Private Key.
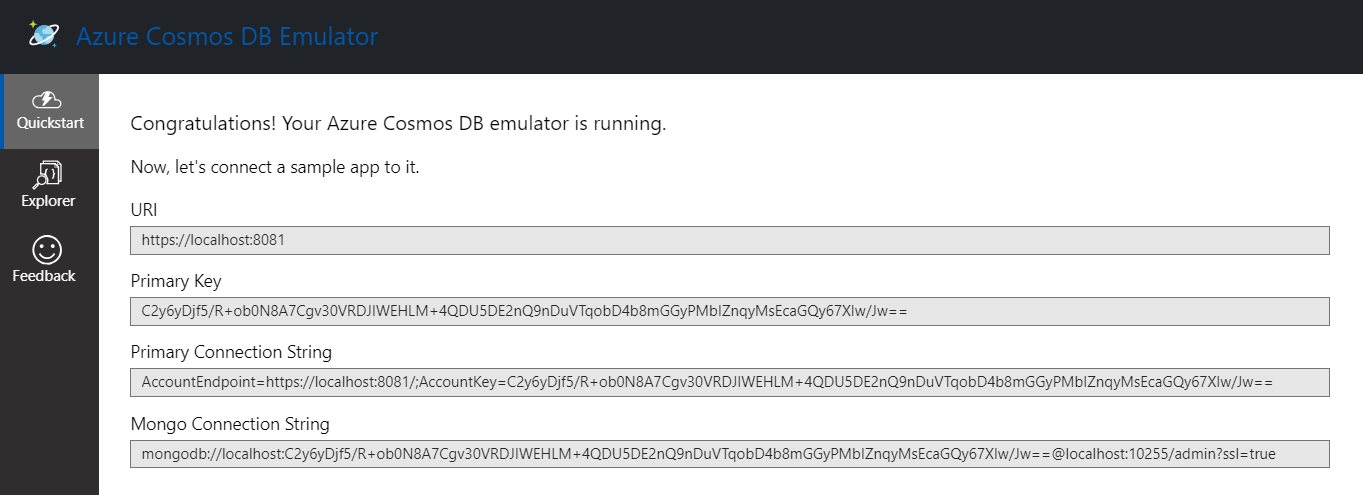
Here is my model class, the Id property type is string, provider will generate the Id automatically.
public class Bookmark
{
[Key]
public string Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public string Image { get; set; }
public string Url { get; set; }
public string CreatedOn { get; set; } = DateTime.UtcNow.ToString();
}And here is the DbContext class, in this class OnModelCreating method is important, without this Cosmos DB driver can’t get the collection name from entity class.
public class BookmarksDbContext : DbContext
{
public BookmarksDbContext(DbContextOptions options) : base(options)
{
}
protected BookmarksDbContext()
{
}
public DbSet<Bookmark> Bookmarks { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Bookmark>();
var bookmarks = modelBuilder.Entity<Bookmark>().Metadata;
bookmarks.CosmosSql().CollectionName = nameof(Bookmarks);
}
}Now you can use the DbContext object in controller class and execute the CRUD operations. Also you need to create the Database and Collection in the emulator, otherwise it won’t work properly. Here is the POST implementation.
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class BookmarksController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly BookmarksDbContext _bookmarksDbContext;
public BookmarksController(BookmarksDbContext bookmarksDbContext)
{
_bookmarksDbContext = bookmarksDbContext;
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<IActionResult> Post([FromBody] Bookmark bookmark)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest();
}
_bookmarksDbContext.Bookmarks.Add(bookmark);
await _bookmarksDbContext.SaveChangesAsync();
return CreatedAtAction(nameof(Get),new{ id = bookmark.Id }, bookmark);
}
}Here is the Postman request
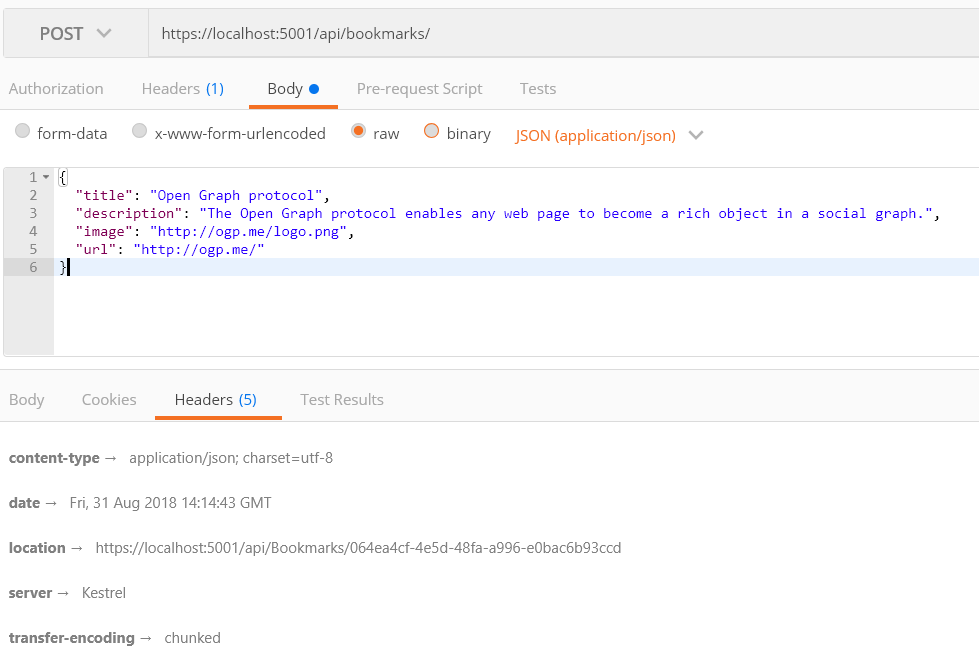
And here is the data in Cosmos DB Emulator.
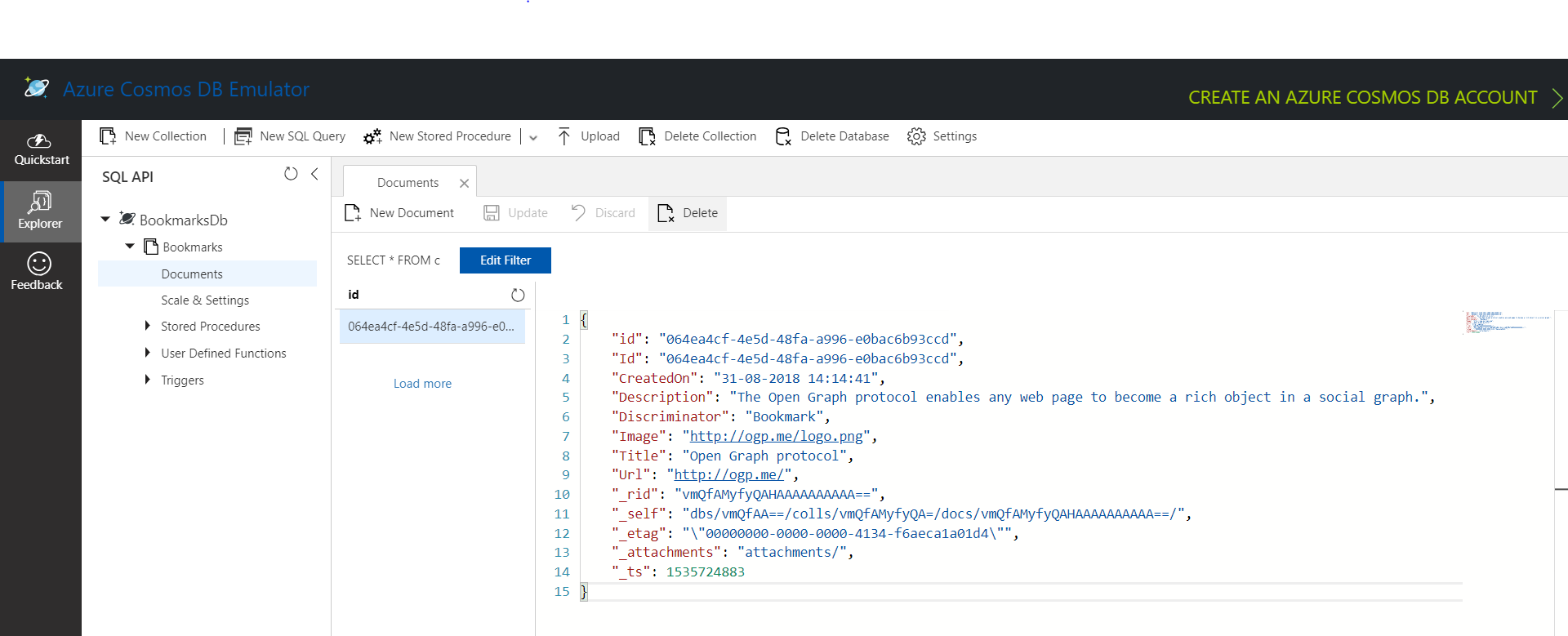
The Cosmos DB SQL provider is in preview, so the API may change in future. You can find the source code of this post in here. If you face any issues in the implementation, let me know.
Happy Programming :)
Found this useful? Share it with your network!
Copyright © 2026 Anuraj. Blog content licensed under the Creative Commons CC BY 2.5 | Unless otherwise stated or granted, code samples licensed under the MIT license. This is a personal blog. The opinions expressed here represent my own and not those of my employer. Powered by Jekyll. Hosted with ❤ by GitHub
