Getting started with GraphQL in ASP.NET Core
November 15, 2021 by Anuraj
AspNetCore GraphQL DotNet6
This post is about GraphQL in ASP.NET Core. GraphQL is a query language for APIs and a runtime for fulfilling those queries with your existing data. GraphQL provides a complete and understandable description of the data in your API, gives clients the power to ask for exactly what they need and nothing more, makes it easier to evolve APIs over time, and enables powerful developer tools. GraphQL implemented using HotChocolate package. To get started, create an empty web project using dotnet web command and then add reference of HotChocolate.AspNetCore package using dotnet add package HotChocolate.AspNetCore command. Once it is done, you can modify the program.cs file like following. I am using .NET 6.0 for this. So there is no Startup.cs and configure and configureservices() methods.
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddGraphQLServer();
var app = builder.Build();
app.MapGet("/", () => "Hello World!");
app.UseRouting();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapGraphQL();
});
app.Run();Now you’re configured GraphQL endpoint. You can run the application and verify you’re able to see the /graphql endpoint. It will display an empty screen like this since we haven’t configured anything.
Unlike REST API, GraphQL always provides only one endpoint. And all the operations are executed against this endpoint. For reading data, we use Query operation, and Creating, Updating and Deleting we use Mutation operation. And for real time notifications, we use Subscription operation. As we haven’t configured any of these it will throw error. Next we will create a Query operation. For this demo I am not using EF Core. So I created two model classes and implemented Query class.
public class Link
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Url { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public string ImageUrl { get; set; }
public DateTime CreatedOn { get; set; }
public ICollection<Tag> Tags { get; set; } = new List<Tag>();
}
public class Tag
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int LinkId { get; set; }
public Link Link { get; set; }
}
public class Query
{
public IQueryable<Link> Links => new List<Link>
{
new Link
{
Id = 1,
Url = "https://example.com",
Title = "Example",
Description = "This is an example link",
ImageUrl = "https://example.com/image.png",
Tags = new List<Tag> { new Tag(){ Name = "Example" } },
CreatedOn = DateTime.Now
},
new Link
{
Id = 2,
Url = "https://dotnetthoughts.net",
Title = "DotnetThoughts",
Description = "DotnetThoughts is a blog about .NET",
ImageUrl = "https://dotnetthoughts.net/image.png",
Tags = new List<Tag>
{
new Tag(){ Name = "Programming" },
new Tag(){ Name = "Blog" },
new Tag(){ Name = "dotnet" }
},
CreatedOn = DateTime.Now
},
}.AsQueryable();
}And add the query type to the Http Pipeline like this.
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddGraphQLServer().AddQueryType<Query>();
var app = builder.Build();
app.MapGet("/", () => "Hello World!");
app.UseRouting();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapGraphQL();
});
app.Run();Now you can run the app again and check the /graphql endpoint again. You will be able to see empty screen again. Then choose the Schema Reference option from the Operations dropdown.
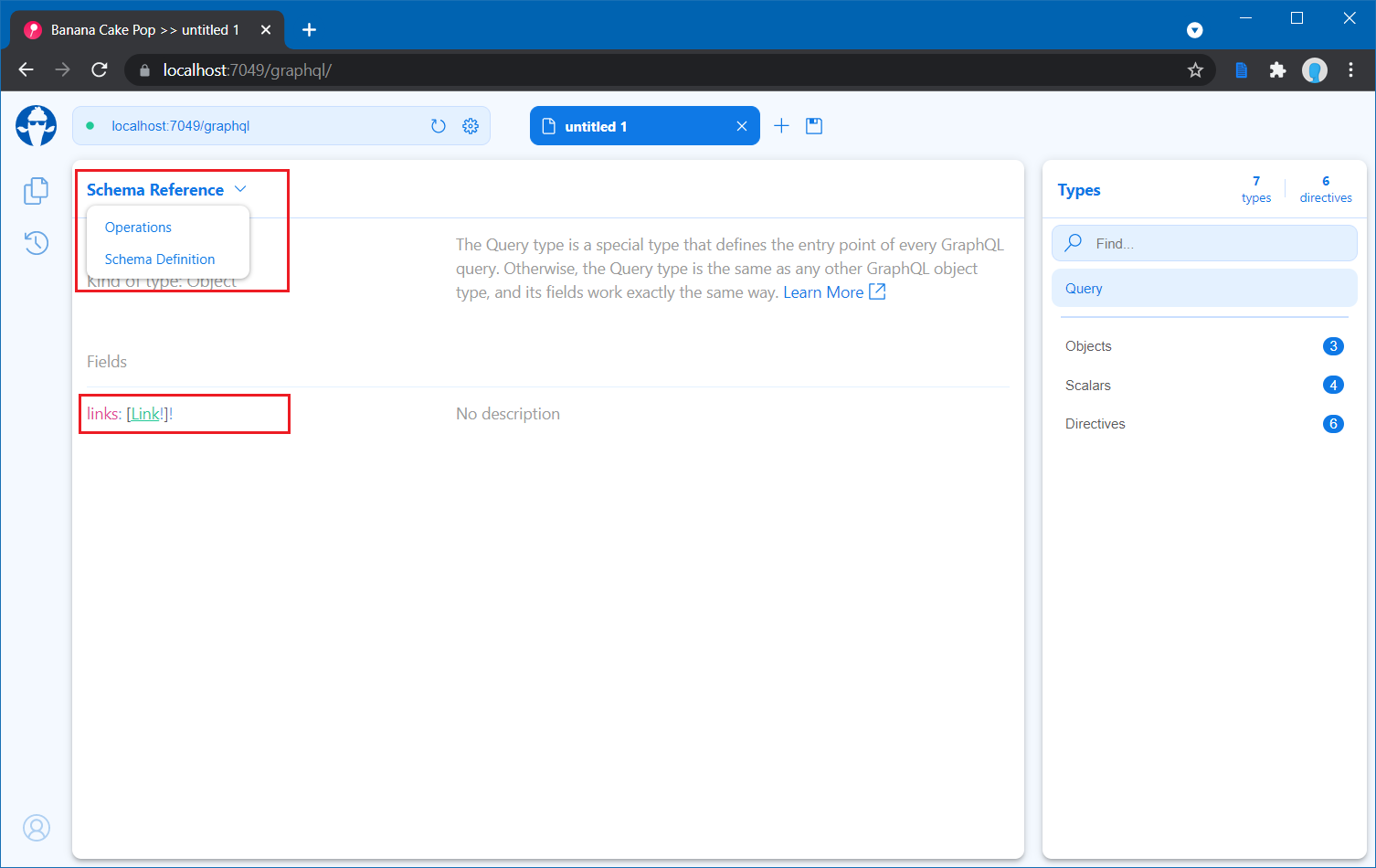
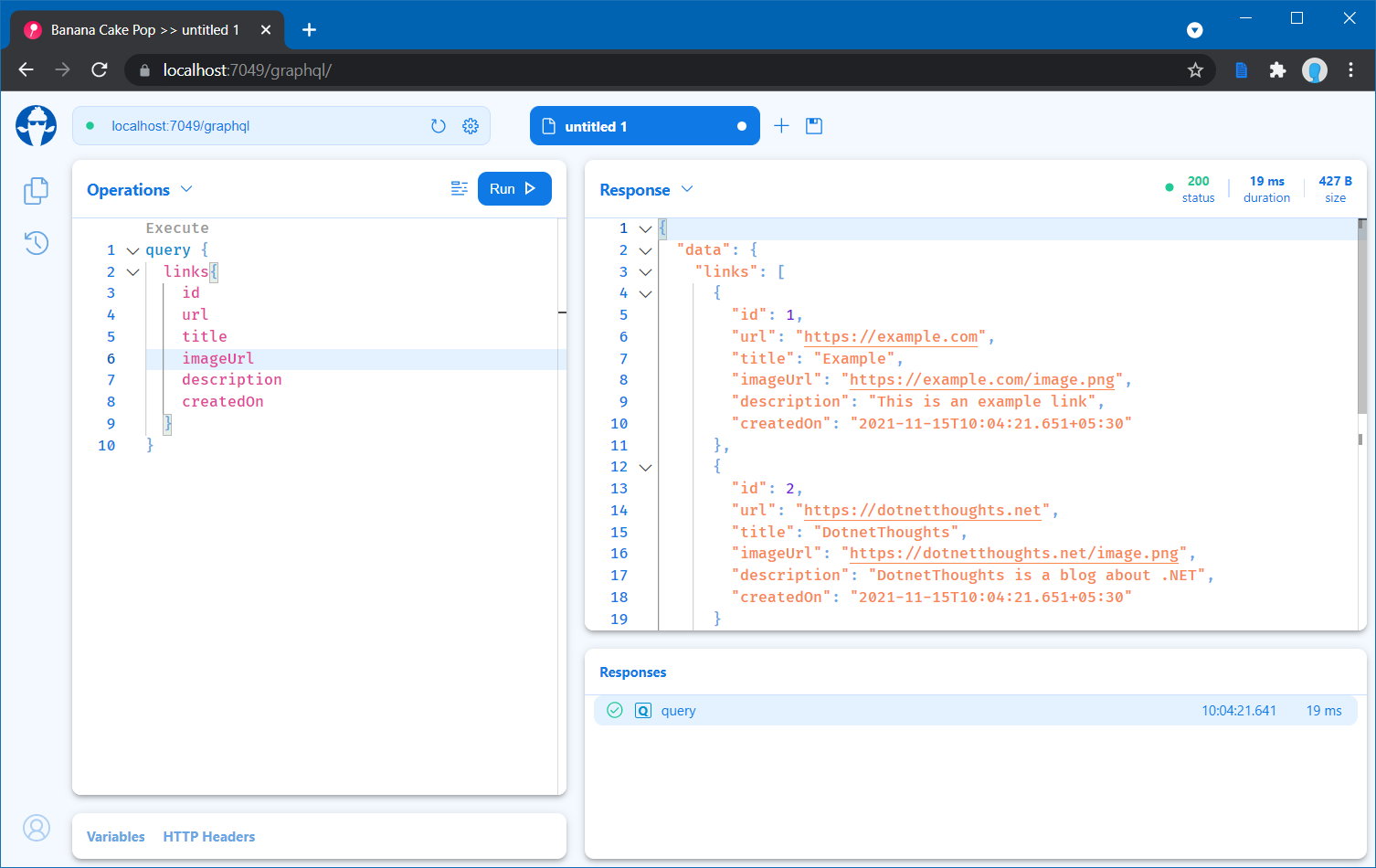
There you will be able to see the GraphQL schema of the Query. Next let us execute a Query and fetch some data. Select the Operations tab. And you can write the following code.
query {
links{
id
url
title
imageUrl
description
createdOn
}
}Which will execute the Query and display result like this.
The one major advantage of GraphQL over REST is client can decide which of the fields it requires. In case of REST if there is an endpoint like which returns links, it will always returns all the fields which the API developer configured - even if the consumer application is not using them. But incase of GraphQL consuming client can decide which all fields required and query those fields only. For example, if the app requires only Title and Image URL, app can send a query like this.
query {
links{
title
imageUrl
}
}It will only return those fields.
GraphQL got lot of advantages like this which can be used to improve your application and API performance. In the upcoming blog posts we will discuss about using EF Core along with GraphQL, Mutations and Subscriptions in GraphQL.
I have implemented all these operations on top of Minimal APIs in .NET 6.0. You can find the source code in GitHub
Happy Programming :)
Found this useful? Share it with your network!
Copyright © 2026 Anuraj. Blog content licensed under the Creative Commons CC BY 2.5 | Unless otherwise stated or granted, code samples licensed under the MIT license. This is a personal blog. The opinions expressed here represent my own and not those of my employer. Powered by Jekyll. Hosted with ❤ by GitHub
