Integrating AWS with .NET Aspire
January 15, 2026 by Anuraj
dotnet aws aspire cloudnative
In this blog post we will learn how to integrate AWS with .NET Aspire. .NET Aspire is an open-source, cloud-native application stack introduced by Microsoft (announced at Build 2023, GA in May 2024). It provides tools, templates, orchestration, and built-in observability so developers can focus on business logic instead of complex infrastructure setup.
First we will be creating a Aspire starter project. I am using the following command dotnet new aspire-starter --use-redis-cache --name HelloAspireAws --output HelloAspireAws. Once it is created, we can run the application using the command dotnet run command with --project parameter HelloAspireAws.AppHost. And when debugging with Visual Studio or VS Code, we need to set the AppHost project as the startup project. When the AppHost is launched for debugging, the Redis container and .NET projects will all be started. .NET Aspire provides the service discovery for the frontend project to locate the Redis container and Web API project. We need to start Docker since we are using Redis for caching. For the integration with AWS, we need the Aspire.Hosting.AWS nuget package - this package helps developers to provision AWS resources as part of the inner dev loop of building applications. The AWS resources can be defined using either a CloudFormation template or the Cloud Development Kit (CDK). We can reference the nuget package using dotnet add package Aspire.Hosting.AWS command. We need to add reference to the AppHost project.
In this blog post I will be using CDK to provision resources. To do that, we can add the following code.
var awsConfig = builder.AddAWSSDKConfig()
.WithProfile("personal")
.WithRegion(RegionEndpoint.APSouth1);
var stack = builder.AddAWSCDKStack("aspire-aws-stack")
.WithReference(awsConfig);
var bucket = stack.AddS3Bucket("images-bucket");
This code configures and provisions AWS infrastructure using .NET Aspire’s AWS integration. It starts by creating an AWS configuration resource that specifies the personal credentials profile and the Asia Pacific Mumbai region (ap-south-1). This configuration is then referenced by an AWS CDK stack named aspire-aws-stack, which serves as a container for defining cloud resources through Infrastructure as Code. Within this stack, an S3 bucket resource is defined with the logical name “images-bucket”.
When the Aspire application runs, it uses the specified credentials to generate CloudFormation templates from the CDK stack definition and deploys them to AWS, resulting in the actual creation of the S3 bucket in your account. This declarative approach allows developers to define their cloud infrastructure alongside their application code in a type-safe manner, with Aspire handling the orchestration of resource provisioning during deployment.
Next in the API Service we can add reference of the S3 bucket and we will able to consume it from the API Service. Here is the AppHost.cs code which adds the reference of bucket to the API project like this.
var cache = builder.AddRedis("cache");
var apiService = builder.AddProject<Projects.HelloAspireAws_ApiService>("apiservice")
.WithHttpHealthCheck("/health")
.WithReference(bucket)
.WaitFor(bucket);
builder.AddProject<Projects.HelloAspireAws_Web>("webfrontend")
.WithExternalHttpEndpoints()
.WithHttpHealthCheck("/health")
.WithReference(cache)
.WaitFor(cache)
.WithReference(apiService)
.WaitFor(apiService);
builder.Build().Run();
Now we can run the app and we will be able to see the resources provisioned.
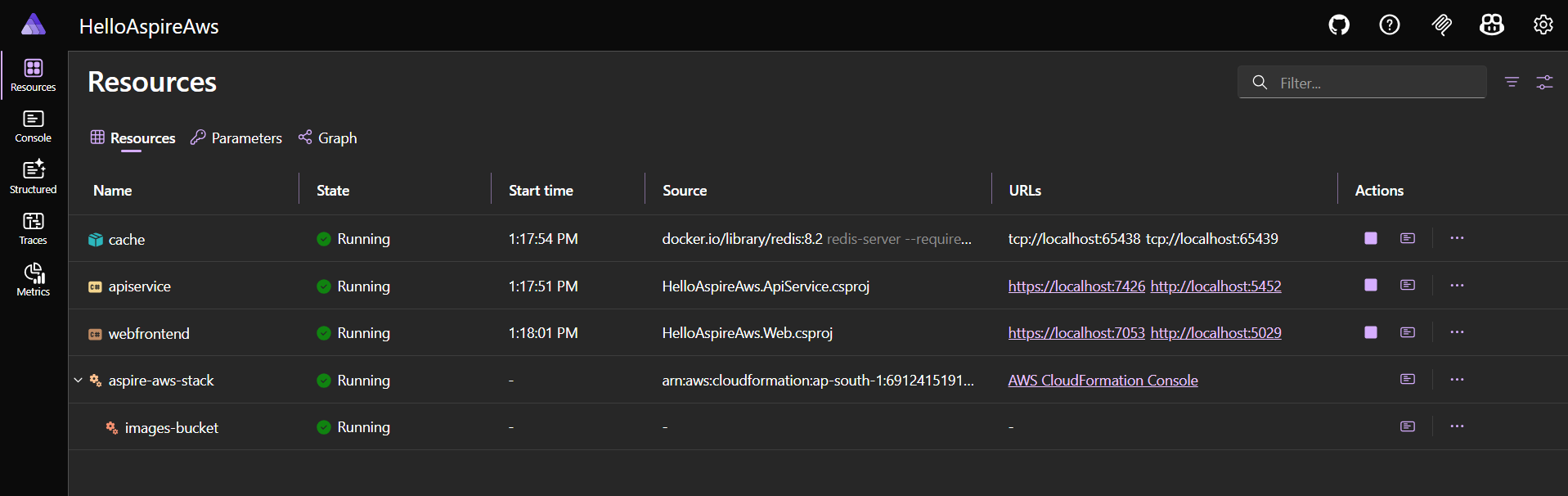
Since we added the reference of the AWS S3 bucket to API, we can consume it from the API using the following code.
builder.Services.AddScoped<IAmazonS3>(sp =>
{
var config = sp.GetRequiredService<IConfiguration>();
// AWS:Region is automatically injected by .NET Aspire's AWS configuration
var region = config["AWS:Region"];
return new AmazonS3Client(RegionEndpoint.GetBySystemName(region));
});
In this code, I am using the AWSSDK.S3 nuget package to create instance of AmazonS3Client. The AWS:Region configuration injected by .NET Aspire. And here is the implementation code.
app.MapGet("/upload-weather-forecast",async ([FromServices] IAmazonS3 s3client,
IConfiguration configuration) =>
{
var bucketName = configuration["AWS:Resources:images-bucket:BucketName"];
var forecast = Enumerable.Range(1, 5).Select(index =>
new WeatherForecast
(
DateOnly.FromDateTime(DateTime.Now.AddDays(index)),
Random.Shared.Next(-20, 55),
summaries[Random.Shared.Next(summaries.Length)]
))
.ToArray();
var request = new PutObjectRequest
{
BucketName = bucketName,
Key = "weather-forecast.json",
ContentType = "application/json",
ContentBody = JsonSerializer.Serialize(forecast)
};
await s3client.PutObjectAsync(request);
return Results.Ok("File uploaded successfully.");
})
.WithName("UploadWeatherForecast");
This way we will be able to integrate AWS with .NET Aspire. I am using AWS profile named personal for this blog post. We can create profiles using aws configure with --profile parameter.
Happy Programming.
Found this useful? Share it with your network!
Copyright © 2026 Anuraj. Blog content licensed under the Creative Commons CC BY 2.5 | Unless otherwise stated or granted, code samples licensed under the MIT license. This is a personal blog. The opinions expressed here represent my own and not those of my employer. Powered by Jekyll. Hosted with ❤ by GitHub
